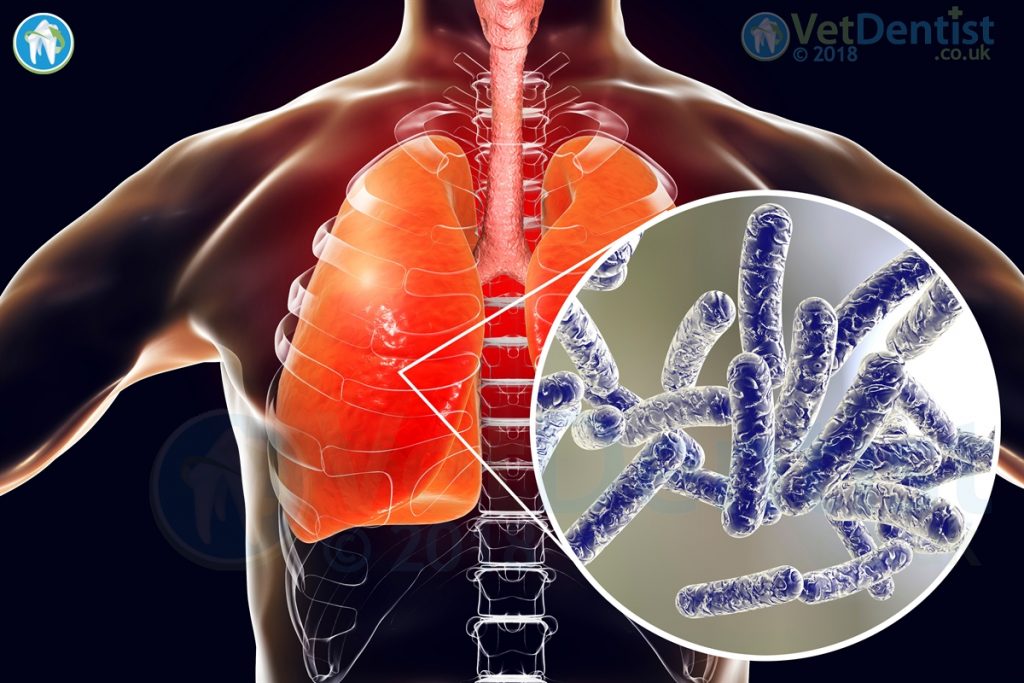
Legionella bacteria appear throughout the environment. One particular species Legionella pneumophilia can invade macrophages, replicating inside them. This may account for its pathogenic capabilities.
Infection arises from inhalation of contaminated aerosols, typically from showers, humidifiers, taps or cooling stations. Dental scalers and high speed drills are other obvious sources of aerosols.
Signs of infection can be absent. Infections may simply result in asymptomatic, self-limiting infections. Others may suffer a flu like illness, with fever, aches and pains. This Pontiac Fever may also be self-limiting and may often be misdiagnosed as being viral influenza. Some individuals can develop pneumonia which can prove fatal.
Legionella prefers to grow at temperatures between 20-45⁰C, the average temperature of dental unit water lines (DUWLs) is 23⁰C. In addition Legionella can survive in lightly chlorinated water, this could result from the bacteria invading protozoa in the water lines.
Potential Issues with Dental Units
Legionella species have been isolated from 68% of Dental Unit Water Lines (DUWLs). 8% of DUWLs yielded the pathogenic strain L. pneumophila.
The death of an 81 year old Italian patient was linked to a Legionella infection contracted from her dentist’s DUWL.
A Californian dentist died from a strain of Legionella linked to his practice’s DUWL.